Income Statement Example: Guide With Simple Examples
If you want to understand business finances, learning from a clear income statement example is the best place to start. Many people find accounting confusing, but when you see real examples with explanations, everything becomes easier.
An income statement shows how much money a business earns, how much it spends, and whether it makes a profit or a loss. Business owners, students, freelancers, and investors all rely on income statements to make smart decisions. In this guide, you will find multiple income statement examples, simple formats, and step-by-step explanations written for beginners.
By the end of this article, you will fully understand how an income statement works and how you can prepare one yourself.

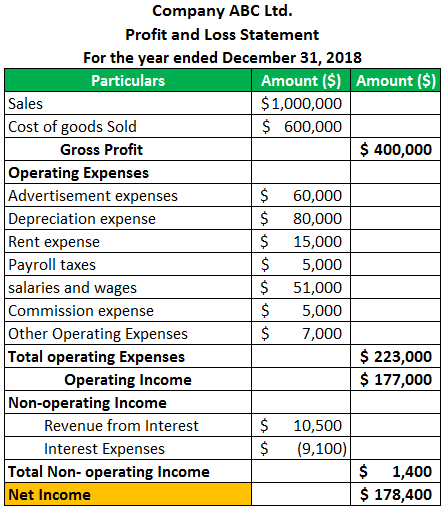
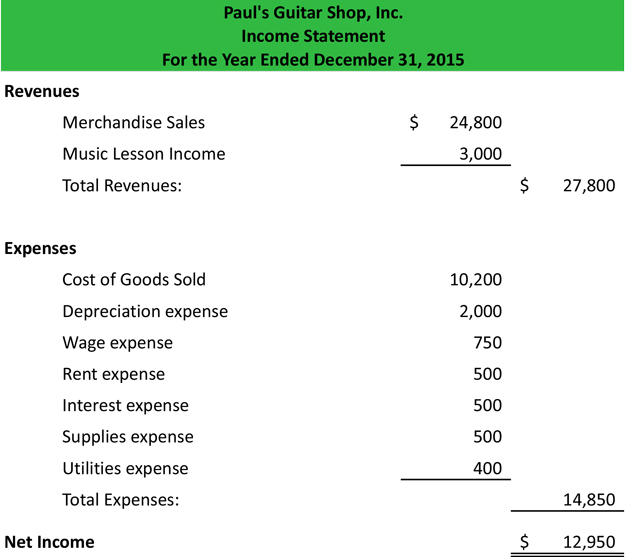
What Is an Income Statement?
An income statement is a financial document that summarizes a business’s income and expenses over a specific period. People also call it a profit and loss statement or statement of earnings.
The main purpose of an income statement is simple:
It tells you whether a business is profitable or not.
An income statement answers questions such as:
- How much revenue did the business generate?
- How much did it spend to operate?
- How much profit or loss occurred?
Unlike other financial statements, an income statement focuses only on performance, not ownership or assets.
Why Income Statements Matter for Businesses
Every successful business relies on income statements. Without them, business owners operate blindly.
Here is why income statements are so important:
- They show true business performance
- They help control unnecessary expenses
- They support tax filing and compliance
- They attract investors and lenders
- They help with pricing and budgeting decisions
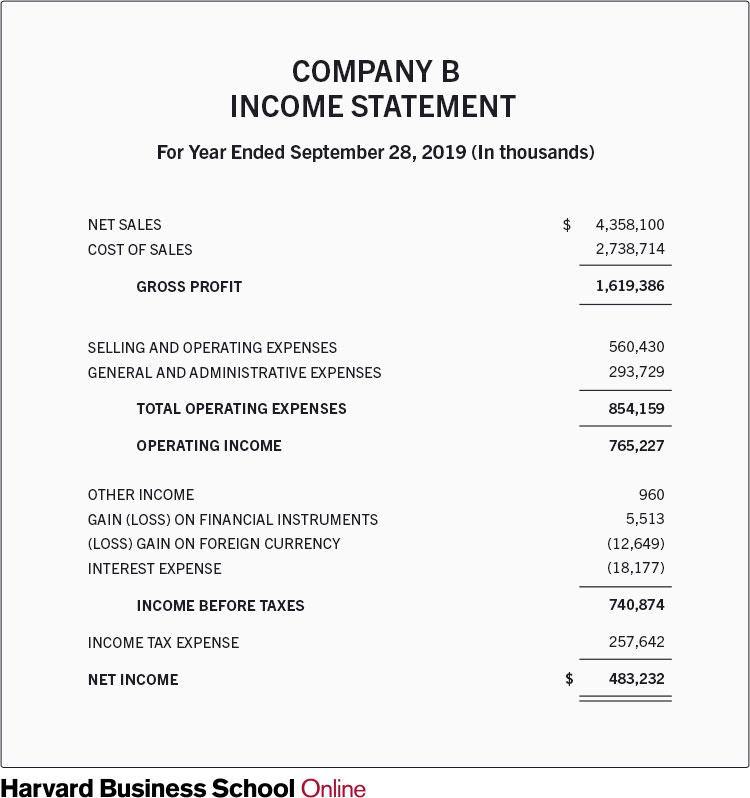
Even small businesses and freelancers benefit from preparing regular income statements.
Key Components of an Income Statement
Before reviewing an income statement example, you must understand its main components. Almost every income statement follows this structure.
1. Revenue
Revenue represents total income earned from selling products or services. It does not include expenses.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS includes direct costs required to produce goods or deliver services, such as materials and labor.
3. Gross Profit
Gross Profit = Revenue − Cost of Goods Sold
This number shows how efficiently a business produces its goods or services.
4. Operating Expenses
Operating expenses include rent, salaries, utilities, advertising, internet, and office supplies.
5. Operating Income
Operating Income = Gross Profit − Operating Expenses
This shows profit from normal business activities.
6. Net Income
Net Income is the final profit after subtracting taxes, interest, and other non-operating costs.
Simple Income Statement Example (Basic Format)
Let’s start with a simple income statement example that beginners can easily understand.
Basic Income Statement Example
| Description | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Revenue | 60,000 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 25,000 |
| Gross Profit | 35,000 |
| Operating Expenses | 18,000 |
| Operating Income | 17,000 |
| Taxes | 4,000 |
| Net Income | 13,000 |
Explanation
- The business earned $60,000 in total revenue.
- It spent $25,000 to produce goods.
- Gross profit equals $35,000.
- Operating expenses reduced profit to $17,000.
- After taxes, the final net income is $13,000.
This income statement example clearly shows how profits decrease step by step.
Income Statement Example for a Small Business
Small businesses usually operate with limited resources, so tracking income and expenses becomes even more important.
Small Business Income Statement Example
| Description | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Sales Revenue | 40,000 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 14,000 |
| Gross Profit | 26,000 |
| Rent | 4,000 |
| Salaries | 7,000 |
| Utilities | 1,200 |
| Marketing | 2,300 |
| Internet & Software | 1,000 |
| Total Expenses | 15,500 |
| Net Income | 10,500 |
Why This Example Is Useful
This income statement example for small business owners shows:
- Realistic operating expenses
- Clear profit calculation
- Easy structure for monthly reporting
Small business owners should prepare income statements every month to avoid cash flow problems.
Income Statement Example for a Service Business
Service businesses have different cost structures compared to product-based businesses.
Service Business Income Statement Example
| Description | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Service Revenue | 30,000 |
| Direct Labor Costs | 8,000 |
| Gross Profit | 22,000 |
| Office Rent | 3,000 |
| Marketing | 1,500 |
| Utilities | 800 |
| Miscellaneous | 700 |
| Total Expenses | 6,000 |
| Net Income | 16,000 |
This income statement example highlights how service businesses often enjoy higher gross margins.
Monthly Income Statement Example
A monthly income statement helps businesses track short-term performance.
Monthly Income Statement Example
| Description | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Revenue | 12,000 |
| Expenses | 8,500 |
| Net Income | 3,500 |
Monthly statements help identify problems early and allow faster decision-making.
Annual Income Statement Example
An annual income statement summarizes the entire year.
Annual Income Statement Example
| Description | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Total Revenue | 150,000 |
| Total Expenses | 110,000 |
| Net Income | 40,000 |
Annual income statements are essential for taxes, investors, and long-term planning.
How to Prepare an Income Statement Step by Step
You do not need to be an accountant to prepare an income statement. Follow these steps carefully.
Step 1: Choose the Time Period
Decide whether you want a monthly, quarterly, or annual income statement.
Step 2: Calculate Revenue
Add all sales and service income earned during the period.
Step 3: Calculate Cost of Goods Sold
Include all direct production or service costs.
Step 4: Find Gross Profit
Subtract COGS from revenue.
Step 5: List Operating Expenses
Write down every business expense, even small ones.
Step 6: Calculate Operating Income
Subtract operating expenses from gross profit.
Step 7: Subtract Taxes and Interest
This final calculation gives you net income.
This process ensures accuracy and consistency.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Income Statement Examples
Many beginners make avoidable mistakes when preparing income statements.
Avoid these errors:
- Mixing personal and business expenses
- Forgetting cash expenses
- Overstating revenue
- Ignoring depreciation
- Not updating statements regularly
Accurate income statements build trust with banks and investors.
Income Statement Template
Using a template saves time and reduces mistakes.
A good income statement template includes:
- Pre-labeled rows
- Automatic formulas
- Monthly and yearly views
You can create one in Excel or Google Sheets in minutes.
Income Statement vs Balance Sheet (Simple Comparison)
| Feature | Income Statement | Balance Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures profit | Shows financial position |
| Time Frame | Over a period | At one point |
| Focus | Income & expenses | Assets & liabilities |
Both reports work together for complete financial analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions About Income Statement Example
What is the simplest income statement example?
A simple income statement includes only revenue, expenses, and net income.
Is income statement the same as profit and loss statement?
Yes, both terms refer to the same financial report.
Do freelancers need income statements?
Yes, income statements help freelancers track profit and prepare taxes.
How often should income statements be prepared?
Most businesses prepare them monthly and annually.
Can I create an income statement without software?
Yes, you can create one manually using spreadsheets.
Final Conclusion
An income statement is one of the most powerful financial tools for any business. This detailed income statement example guide shows how money flows through a business from revenue to net profit. When you understand income statements, you gain control over expenses, improve profitability, and make smarter financial decisions.